— ARCHIVES —
Exercise of the Month - October 2007:
“Medicine ball chest pass”
Upper body power is something many people, athletes included, severely lack. While many exercise enthusiasts flock to the bench press, dumbbell incline press, and push-ups in an effort to improve their upper body power, they are clearly missing the boat. While the aforementioned exercises certainly develop upper body strength and endurance, they don’t do nearly as much to improve upper body power.
Enter- medicine ball training.
Medicine balls have been used for many years with athletes and laypersons as well to improve upper body power. I actually wrote an article in November, 2006 where I featured medicine ball chest passes (http://www.pcconditioning.com/articles/Nov2006_basketball.pdf). Clearly in many sports, upper body power is necessary. However, I’ll sometimes use the medicine ball chest pass with non-athlete clients simply because fast twitch muscle fiber recruitment reduces as a person ages.
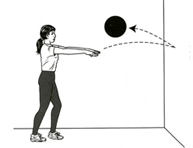 The medicine ball chest pass can either be performed against a wall or with a partner (see pictures). Start with the ball slightly in front of the chest and pass the ball against a wall or to a partner. This exercise should be done 1-3 sets for 6-10 repetitions as part of the “power” portion of your workout, typically performed during the earlier part of your workout since it is neurologically demanding. Power Systems, Inc. recommends the following in terms of size selection for medicine ball exercises:
The medicine ball chest pass can either be performed against a wall or with a partner (see pictures). Start with the ball slightly in front of the chest and pass the ball against a wall or to a partner. This exercise should be done 1-3 sets for 6-10 repetitions as part of the “power” portion of your workout, typically performed during the earlier part of your workout since it is neurologically demanding. Power Systems, Inc. recommends the following in terms of size selection for medicine ball exercises:
Ball sizes (weight in lbs.) |
Recommended Use |
2-6 lbs. |
Beginner athletes, fitness classes, one-handed exercises |
8-12 lbs. |
Intermediate athletes, advanced fitness classes, passing exercises |
12-18 lbs. |
Advanced athletes, two-handed throws |


